Search Results
Results for: 'stomach enzyme pepsin'
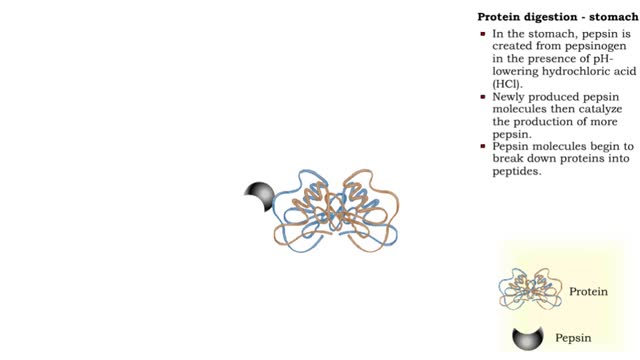
Protein digestion - stomach & small intestine
By: HWC, Views: 6086
• Protein digestion occurs in the stomach and small intestine. • The stomach enzyme pepsin initiates the process. • Pancreatic and intestinal brush border enzymes complete the digestive process. • In the stomach, pepsin is created from pepsinogen in the presence of pH-lowering hyd...
Digestive chemicals - water, gastric acid, bile & bicarbonate
By: HWC, Views: 6359
• Water is the most abundant molecule in ingested fluids. • Water plays a primary role in hydrolytic digestive reactions. • Helps liquefy and transport digestive foodstuffs down the tract. • Transports secretions from accessory digestive organs to gastrointestinal tract. • Aids ...
By: HWC, Views: 6642
The endocrine system maintains many body conditions within normal limits with feedback loops. Each endocrine feedback loop maintains homeostasis using the following components: • Stimulus - a change in a body condition. • Production cell - an endocrine cell that produces a hormone after b...
By: HWC, Views: 6141
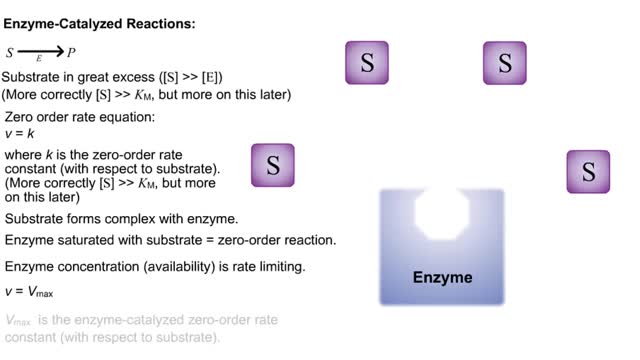
S P Substrate in great excess ([S] -- [E]) (More correctly [S] -- KM, but more on this later) Zero order rate equation: v = k where k is the zero-order rate constant (with respect to substrate). (More correctly [S] -- KM, but more on this later) Substrate forms complex with enzyme. ...
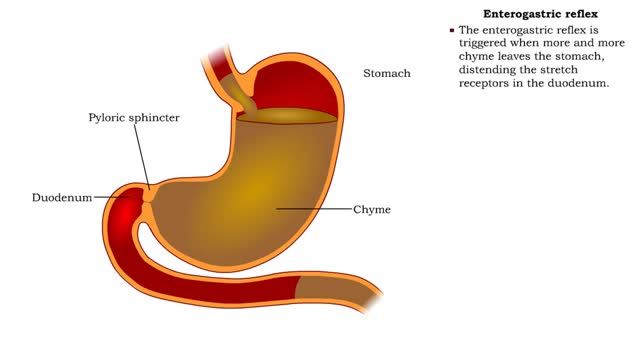
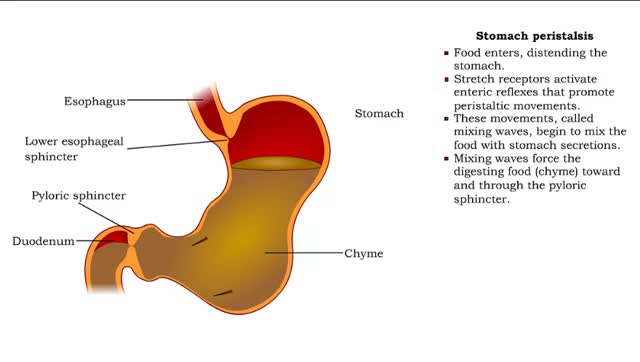
Stomach peristalsis & Enterogastric reflex
By: HWC, Views: 6070
• Food enters, distending the stomach. • Stretch receptors activate enteric reflexes that promote peristaltic movements. • These movements, called mixing waves, begin to mix the food with stomach secretions. • Mixing waves force the digesting food (chyme) toward and through the pylo...
Stomach peristalsis - Movement of Food Through the Small Intestine
By: HWC, Views: 6673
Peristalsis is a series of wave-like muscle contractions that moves food to different processing stations in the digestive tract. The process of peristalsis begins in the esophagus when a bolus of food is swallowed. The strong wave-like motions of the smooth muscle in the esophagus carry the food...
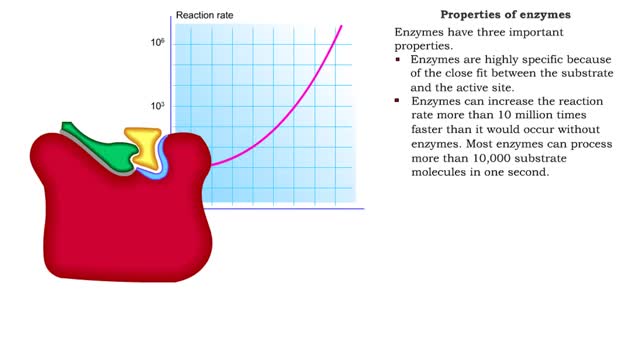
Enzyme structure - Properties of enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 6594
■ Enzymes are proteins that catalyze reactions. ■ Some enzymes have two parts: a protein or apoenzyme and a non-protein or cofactor. ■ Cofactor can be a metal ion or another organic molecule called a coenzyme. ■ Coenzymes often come from vitamins. ■ Cofactors affect the shape of...
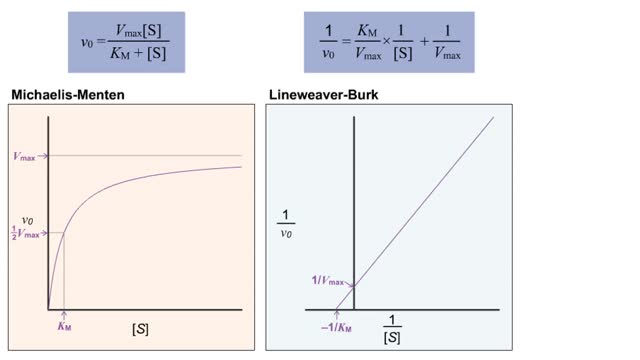
Virtual Enzyme Kinetics & Lineweaver Burk Plot
By: HWC, Views: 6216
• The double-reciprocal (also known as the Lineweaver-Burk) plot is created by plotting the inverse initial velocity (1/V0) as a function of the inverse of the substrate concentration (1/[S]). • This plot is a useful way to determined different inhibitors such as competitive, uncompetitive...
By: HWC, Views: 6551
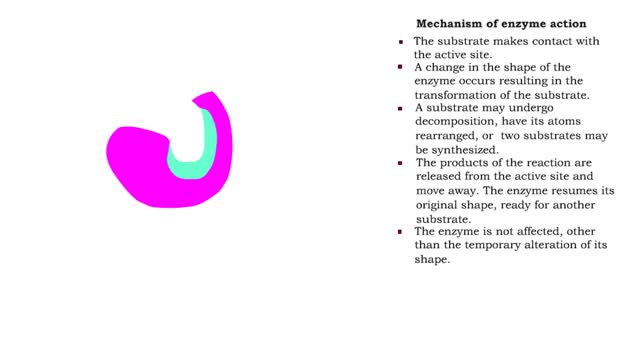
■ The substrate makes contact with the active site. ■ A change in the shape of the enzyme occurs resulting in the transformation of the substrate. ■ A substrate may undergo decomposition, have its atoms rearranged, or two substrates may be synthesized. ■ The products of the reaction...
Advertisement